Our bi-weekly Opinion provides you with latest updates and analysis on major capital market and financial investment industry issues.

ESG Management in Financial Services Firms Illustrated in the Case of Goldman Sachs
Publication date Jun. 15, 2021
Summary
ESG management is a subject of keen attention in the corporate sector, and the financial services industry is no exception. For financial services firms, as a market intermediary, ESG management is even more complex, as it involves not only incorporating ESG factors in its own operations, but also includes ESG assessment and engagement of other firms, along with meeting the ESG demand of investors. Among global financial services firms, Goldman Sachs is among the leaders in actively implementing ESG management. Its ESG management is based on clearly-defined principles, with its organizational structures and processes that ensure ESG integration into its overall business operations. On the other hand, there are numerous challenges to be dealt with for ESG management to take hold more effectively. In particular, the relevant infrastructure and ecosystem should be in place, with qualitative and quantitative improvements in ESG data and disclosure. Furthermore, Korea’s financial services firms have an important role to play in shifting public perception by continuously providing information and facilitating discussion, in order to help expand the demand base for ESG financial products and services.
ESG management—a management style incorporating environmental (E), social (S) and governance (G) factors in business management—has recently been a subject of keen attention in business management, and the financial services sector is no exception to that trend. In particular, ESG management of financial services firms, as a market intermediary, is characterized by efforts to enhance not only their own ESG levels but also that of other firms. The underlying goal of ESG management is to address a wide array global issues, such as climate change and social inequality. The role of financial services firms towards that end is to help allocate capital more effectively and efficiently. Accordingly, ESG management of financial services companies cover a diverse range of activities, such as producing and analyzing ESG data, financing ESG projects, and providing financial products and services incorporating ESG factors.
For a better understanding of ESG management of financial services firms, it is worth looking at the case of Goldman Sachs. Along with BlackRock, Goldman Sachs is counted among the leaders in ESG management. The term “ESG” was first mentioned in the 2005 UN Global Compact report titled “Who Cares Wins”, which presented possible impacts of non-financial factors, such as environmental, social and governance, on the long-term performance of businesses. Goldman Sachs was one of the financial firms responsible for the key analyses in the report. In the wake of the report, Goldman Sachs began developing a system factoring ESG elements in company analysis, which later evolved into GS Sustain. Furthermore, Goldman Sachs is one of the first major global investment banks publishing the sustainability report that meets the guidance of the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
Goldman Sachs’s ESG management principles and processes
The Environmental Policy Framework, established in 2005, stipulates Goldman Sachs’s key ESG management principles. The gist of the principles is that firms should perceive environmental and social factors on top of financial factors, such as market and credit risks, as a material risk and take them into account in business decisions. To that end, Goldman Sachs formulated guidelines that help quantitatively and qualitatively assess ESG risks. Also, Goldman Sachs put in place a process to review environmental and social risks on top of financial factors before making business selection decisions under the guidelines. Transactions with high environmental and social risks are subject to enhanced review before they are approved or rejected. The final business selection decision involves additional risk analysis and discussion among key officials where necessary.1)

Goldman Sachs’s ESG principles are also reflected in its stewardship code and IPO policy. A particular emphasis for Goldman Sachs is employee diversity. Since 2020, the stewardship code of Goldman Sachs Asset Management established a provision to vote against the board if it does not have at least one female member.2) Also, the company’s investment banking unit set up a principle to only underwrite IPOs of private companies that have at least one female board member. Goldman Sachs’s stewardship code and IPO policy with regard to ESG are considered strict even by the standard of global financial firms.
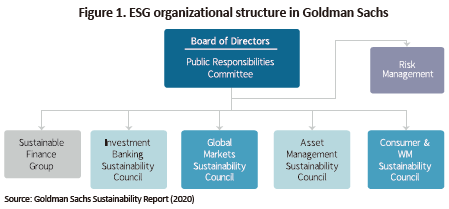
Goldman Sachs set up its organizational structure to help implement its ESG policies. Within the board of directors, the Public Responsibilities Committee is responsible for dealing with ESG issues. Furthermore, each of the company’s four major business operations has a sustainability council. Importantly, each sustainability council is led by a senior partner who is given adequate powers and responsibilities. In addition, Goldman Sachs is continuously recruiting experts for each business unit, aiming to strengthen its ESG capabilities. In 2019, it established the Sustainable Financial Group that is dedicated to coordinate firmwide ESG activities, and appointed John Goldstein—an experienced ESG expert—to lead the group.3) Although Goldman Sachs boasts the world’s best financial business capabilities, it is still seeking to gain more expertise in ESG by aggressively recruiting external experts.
ESG operations of Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs has made endeavor to holistically integrate ESG into its existing business operations and to develop new business opportunities. In investment banking, it is incorporating ESG factors in each business, for example, financing via green bond issuance, advising ESG-related M&A deals, providing research coverage on ESG firms and industries, and so on. The firm’s brokerage arm—the Global Markets unit—is providing diverse services for a wide array of asset classes, such as development of ESG investment strategies, market making for diverse ESG assets, tools for analyzing ESG portfolios, to name a few. ESG is also fully embedded in the Asset Management unit that is providing financial investment products such as ESG funds, and actively engaged in proxy voting and engagement. The Consumer & Wealth Management operation is also offering their retail customers a diverse range of financial investment products including ESG funds, ESG ETFs, and bespoke ESG portfolios.
Financial firms such as Goldman Sachs, are also helping develop new and innovative ESG financing solutions. One example is the sustainability-linked bonds (SLBs), the fastest-growing ESG financing tool.4) SLBs are a bond instrument that selects ESG-linked key performance indicators (KPI) taking into account issuer-specific factors, and accordingly sets up sustainability performance targets (SPTs). An SLB has a structure where the interest rate remains low if the issuer achieves the predetermined SPT, but goes up if the issuer fails to meet the target.5) Unlike green bonds whose proceeds must be used limitedly for particular ESG projects, the SLB structure allows the issuer to use the proceeds for any of their business operations. This flexibility is one of the reasons for the increasing demand for SLBs. SLBs demonstrate the possibility of a new financing solution that leverages financial firms’ existing capabilities, such as financial analysis and product structuring, in developing new types of ESG funding.
Corporate need to meet ESG goals is also creating new business opportunities for financial services firms. For example, Apple pledged to become carbon neutral by 2030. To meet that goal, Apple estimates its own efforts can reduce 75% of the needed carbon emissions, but needs other ways for the remaining 25%. Apple in 2021 joined hands with Goldman Sachs and Conservation International to establish a $200 million Restore Fund which is expected to remove one million metrics tons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere per year. With Apple a major investor in the fund, Conservation International is responsible for environmental compliance of the projects, while Goldman Sachs is in charge of managing the fund. As more and more firms pledge carbon neutrality, the demand for carbon reduction through financial investing is expected to rise further.
Conclusion
Although ESG management is a growing trend among companies, there are still many hurdles that must be overcome for it to be implemented effectively. The biggest challenge is establishing the ESG infrastructure and ecosystem. Particularly, ESG data and disclosure need to improve in terms of the quantity, quality, and standardization. Also required is the broadening of the demand base for ESG-related financial investment products and services. The cases of other countries show that the major demand for ESG investing expanded first from institutional investors then to firms, and recently the retail market is also beginning to form. Although Korea has a certain level of demand for ESG-related financial services among institutional investors, domestic corporate demand is still at an early stage and the retail market is even smaller. A financial market linked to ESG could expand further only if the public understands ESG better and changes their existing perception. Financial services firms have an important role to play towards that end.
Korea’s financial services firms have also been active in implementing ESG management, for example establishing an ESG committee under the board of directors, and setting up ESG councils. However, more efforts are required for ESG management to take hold effectively. First, firms should establish clear ESG principles that meet their firm-specific conditions and business philosophy. Also needed is formulating a concrete process for executing those principles, as well as procedures and guidelines to resolve internal conflicts of interest that can arise from issues surrounding ESG at the business level. Communication and training programs are needed to enhance firmwide awareness of ESG. Also, ESG capabilities need to be increased by developing internal talent, as well as recruiting external experts. Lastly, a long-term perspective and approach to integrating ESG is the most important factor.
1) https://www.goldmansachs.com/s/environmental-policy-framework
2) Goldman Sachs, 2021, Policy, procedures and guidelines for GSAM global proxy voting: 2021 edition.
3) John Goldstein is the cofounder of leading ESG investing firm Imprint Capital. Seeking to enhance its ESG capabilities, Goldman Sachs acquired Imprint Capital in 2015.
4) Reuters, March 22, 2021, Sustainability-linked bond market to swell up to $150 billion: JPMorgan ESG DCM head.
5) ICMA, 2020, Sustainability-linked bond principles, voluntary process guidelines.
For a better understanding of ESG management of financial services firms, it is worth looking at the case of Goldman Sachs. Along with BlackRock, Goldman Sachs is counted among the leaders in ESG management. The term “ESG” was first mentioned in the 2005 UN Global Compact report titled “Who Cares Wins”, which presented possible impacts of non-financial factors, such as environmental, social and governance, on the long-term performance of businesses. Goldman Sachs was one of the financial firms responsible for the key analyses in the report. In the wake of the report, Goldman Sachs began developing a system factoring ESG elements in company analysis, which later evolved into GS Sustain. Furthermore, Goldman Sachs is one of the first major global investment banks publishing the sustainability report that meets the guidance of the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
Goldman Sachs’s ESG management principles and processes
The Environmental Policy Framework, established in 2005, stipulates Goldman Sachs’s key ESG management principles. The gist of the principles is that firms should perceive environmental and social factors on top of financial factors, such as market and credit risks, as a material risk and take them into account in business decisions. To that end, Goldman Sachs formulated guidelines that help quantitatively and qualitatively assess ESG risks. Also, Goldman Sachs put in place a process to review environmental and social risks on top of financial factors before making business selection decisions under the guidelines. Transactions with high environmental and social risks are subject to enhanced review before they are approved or rejected. The final business selection decision involves additional risk analysis and discussion among key officials where necessary.1)

Goldman Sachs set up its organizational structure to help implement its ESG policies. Within the board of directors, the Public Responsibilities Committee is responsible for dealing with ESG issues. Furthermore, each of the company’s four major business operations has a sustainability council. Importantly, each sustainability council is led by a senior partner who is given adequate powers and responsibilities. In addition, Goldman Sachs is continuously recruiting experts for each business unit, aiming to strengthen its ESG capabilities. In 2019, it established the Sustainable Financial Group that is dedicated to coordinate firmwide ESG activities, and appointed John Goldstein—an experienced ESG expert—to lead the group.3) Although Goldman Sachs boasts the world’s best financial business capabilities, it is still seeking to gain more expertise in ESG by aggressively recruiting external experts.

Goldman Sachs has made endeavor to holistically integrate ESG into its existing business operations and to develop new business opportunities. In investment banking, it is incorporating ESG factors in each business, for example, financing via green bond issuance, advising ESG-related M&A deals, providing research coverage on ESG firms and industries, and so on. The firm’s brokerage arm—the Global Markets unit—is providing diverse services for a wide array of asset classes, such as development of ESG investment strategies, market making for diverse ESG assets, tools for analyzing ESG portfolios, to name a few. ESG is also fully embedded in the Asset Management unit that is providing financial investment products such as ESG funds, and actively engaged in proxy voting and engagement. The Consumer & Wealth Management operation is also offering their retail customers a diverse range of financial investment products including ESG funds, ESG ETFs, and bespoke ESG portfolios.
Financial firms such as Goldman Sachs, are also helping develop new and innovative ESG financing solutions. One example is the sustainability-linked bonds (SLBs), the fastest-growing ESG financing tool.4) SLBs are a bond instrument that selects ESG-linked key performance indicators (KPI) taking into account issuer-specific factors, and accordingly sets up sustainability performance targets (SPTs). An SLB has a structure where the interest rate remains low if the issuer achieves the predetermined SPT, but goes up if the issuer fails to meet the target.5) Unlike green bonds whose proceeds must be used limitedly for particular ESG projects, the SLB structure allows the issuer to use the proceeds for any of their business operations. This flexibility is one of the reasons for the increasing demand for SLBs. SLBs demonstrate the possibility of a new financing solution that leverages financial firms’ existing capabilities, such as financial analysis and product structuring, in developing new types of ESG funding.
Corporate need to meet ESG goals is also creating new business opportunities for financial services firms. For example, Apple pledged to become carbon neutral by 2030. To meet that goal, Apple estimates its own efforts can reduce 75% of the needed carbon emissions, but needs other ways for the remaining 25%. Apple in 2021 joined hands with Goldman Sachs and Conservation International to establish a $200 million Restore Fund which is expected to remove one million metrics tons of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere per year. With Apple a major investor in the fund, Conservation International is responsible for environmental compliance of the projects, while Goldman Sachs is in charge of managing the fund. As more and more firms pledge carbon neutrality, the demand for carbon reduction through financial investing is expected to rise further.
Conclusion
Although ESG management is a growing trend among companies, there are still many hurdles that must be overcome for it to be implemented effectively. The biggest challenge is establishing the ESG infrastructure and ecosystem. Particularly, ESG data and disclosure need to improve in terms of the quantity, quality, and standardization. Also required is the broadening of the demand base for ESG-related financial investment products and services. The cases of other countries show that the major demand for ESG investing expanded first from institutional investors then to firms, and recently the retail market is also beginning to form. Although Korea has a certain level of demand for ESG-related financial services among institutional investors, domestic corporate demand is still at an early stage and the retail market is even smaller. A financial market linked to ESG could expand further only if the public understands ESG better and changes their existing perception. Financial services firms have an important role to play towards that end.
Korea’s financial services firms have also been active in implementing ESG management, for example establishing an ESG committee under the board of directors, and setting up ESG councils. However, more efforts are required for ESG management to take hold effectively. First, firms should establish clear ESG principles that meet their firm-specific conditions and business philosophy. Also needed is formulating a concrete process for executing those principles, as well as procedures and guidelines to resolve internal conflicts of interest that can arise from issues surrounding ESG at the business level. Communication and training programs are needed to enhance firmwide awareness of ESG. Also, ESG capabilities need to be increased by developing internal talent, as well as recruiting external experts. Lastly, a long-term perspective and approach to integrating ESG is the most important factor.
1) https://www.goldmansachs.com/s/environmental-policy-framework
2) Goldman Sachs, 2021, Policy, procedures and guidelines for GSAM global proxy voting: 2021 edition.
3) John Goldstein is the cofounder of leading ESG investing firm Imprint Capital. Seeking to enhance its ESG capabilities, Goldman Sachs acquired Imprint Capital in 2015.
4) Reuters, March 22, 2021, Sustainability-linked bond market to swell up to $150 billion: JPMorgan ESG DCM head.
5) ICMA, 2020, Sustainability-linked bond principles, voluntary process guidelines.
