Find out more about our latest publications

Tightening Financial Conditions and Implications for the Housing Market in Korea
Issue Papers 22-05 Apr. 05, 2022
- Research Topic Macrofinance
- Page 15
In the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic, housing prices have soared amid a rapid increase in household debt stemming from rising housing loans. This has raised concerns about financial imbalances in the housing market. In the meantime, as central banks of major economies normalize their monetary policy due to inflationary concerns, the housing market may be affected by the change in financial conditions. Against this backdrop, this article intends to examine the impact of tightening financial conditions on the housing market and present relevant implications.
This article analyzes the effect of changes in interest rates and household loans on housing price growth. As shown in the analysis, an increase in the base rate contributes to reducing price rises across the housing market. Since the market responds to rate hikes gradually with time, however, household loans are likely to have a bigger impact on housing prices for the short term, compared to interest rates. In an analysis of upside and downside risks to housing prices, the upside risk has increased considerably since the pandemic, driven by a steep rise in household lending and upward price dynamics. In particular, the recent realized growth rate of housing price is close to the right tail (upside risk) of its conditional distribution, suggesting signs of overheating in the market.
Considering the growing uncertainty of the housing market, as evidenced by a surge in the upside risk to housing prices, household loans need to be actively dealt with to curb rocketing housing prices in the short-term. In the long run, Bank of Korea’s policy stance to raise interest rates is expected to put downward pressure on housing prices. Considering the ripple effects of rate hikes, gradual normalization of stricter household loan regulations would be needed in the long-term.
This article analyzes the effect of changes in interest rates and household loans on housing price growth. As shown in the analysis, an increase in the base rate contributes to reducing price rises across the housing market. Since the market responds to rate hikes gradually with time, however, household loans are likely to have a bigger impact on housing prices for the short term, compared to interest rates. In an analysis of upside and downside risks to housing prices, the upside risk has increased considerably since the pandemic, driven by a steep rise in household lending and upward price dynamics. In particular, the recent realized growth rate of housing price is close to the right tail (upside risk) of its conditional distribution, suggesting signs of overheating in the market.
Considering the growing uncertainty of the housing market, as evidenced by a surge in the upside risk to housing prices, household loans need to be actively dealt with to curb rocketing housing prices in the short-term. In the long run, Bank of Korea’s policy stance to raise interest rates is expected to put downward pressure on housing prices. Considering the ripple effects of rate hikes, gradual normalization of stricter household loan regulations would be needed in the long-term.
Ⅰ. 논의배경
코로나19의 경제적 충격에 대응하여 각국 중앙은행은 통화정책을 상당히 완화적으로 운용하였으며 이를 통해 금융시장 안정 및 실물경제 회복에 크게 기여하였다. 그러나 2021년 하반기 이후 인플레이션 우려가 높아짐에 따라 주요국 중앙은행은 정책금리 인상1), 자산매입 종료 등을 통해 통화정책을 빠르게 정상화하는 추세이다.
국내 금융시장도 작년 8월부터 한국은행의 금리인상 기조가 이어지면서 완화적 금융여건이 축소되고 있다. 이러한 금융환경 변화가 자산시장, 특히 주택시장에 미칠 영향에 관심이 높아지고 있다.2) 대부분의 주택매매에서 레버리지가 활용됨에 따라 금융여건의 변화는 주택시장 변동의 주요인으로 작용한다. 팬데믹 이후 주택관련 대출을 중심으로 가계부채가 빠르게 늘어난 가운데 주택가격이 가파른 상승세를 기록하는 등 주택시장을 중심으로 금융불균형에 대한 우려가 높은 상황이다. 따라서 최근 주택시장 변화에 대한 이해는 거시금융안정성 측면에서 중요한 의미를 가진다.
본고에서는 금융환경의 긴축적 변화가 주택시장에 미치는 영향을 분석하고 시사점을 제시하고자 한다. 본 보고서의 구성은 다음과 같다. Ⅱ장에서는 팬데믹 이후 주택가격 추이와 최근 금융환경의 변화를 살펴본다. Ⅲ장에서는 금융환경 변화가 주택가격에 미치는 영향을 분석한다. 먼저 금리인상이 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 분석하고 가계대출의 영향과 비교해본다. 한편 주택시장의 경우, 수요와 공급의 신축적인 조정이 어려워 단기적으로는 가격 변동성이 크게 높아질 수 있다. 팬데믹 이후 주택시장의 불확실성이 크게 높아진 점을 감안하여 분위회귀(quantile regression)를 통해 주택가격의 상방 리스크(upside risk)와 하방 리스크(downside risk)를 분석한다. 마지막 Ⅳ장에서는 분석 내용을 바탕으로 정책적 시사점을 도출한다.
Ⅱ. 팬데믹 이후 주택시장 추이
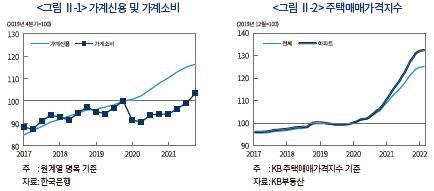
<그림 Ⅱ-1>에 나타난 바와 같이 팬데믹 이후 가계신용이 소비활동에 비해 빠른 속도로 증가하였다. 부채를 통해 늘어난 가계의 유동성은 실물경제로 순환되기보다는 대체로 자산시장으로 유입된 것으로 판단된다. 특히, 부동산시장으로의 자금 유입이 크게 늘어나면서 2020년 이후 주택가격은 과거 추세에 비해 상당히 가파르게 상승하였다(<그림 Ⅱ-2> 참조). 2020~2021년 중 전국 주택매매가격지수와 아파트매매가격지수는 각각 24.6%, 31.8% 상승하였는데, 이는 직전 10년 상승률(2009~2019년 중 각각 23.6%, 27.9%)을 상회한다.
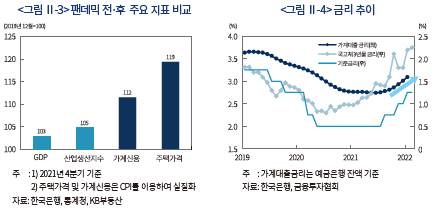
<그림 Ⅱ-3>에서 확인할 수 있듯이 실물경제 회복세와 주택가격 상승세는 큰 괴리를 나타내고 있다. 경기회복세, 저축률 상승 등 경제적 요인에 공급제약 등 수급적인 요인이 더해지면서 주택수요가 확대된 가운데, 완화적 금융환경을 바탕으로 빠르게 늘어난 가계신용이 주택가격 상승을 뒷받침하고 있다.3) 주택시장을 중심으로 금융불균형 누적에 대한 우려가 크게 높아짐에 따라 한국은행은 주요국보다 선제적으로 금리인상을 단행하였으며 금융당국도 가계대출 총량을 적극적으로 관리하고 있다.
목표수준을 상회하는 물가상승세가 지속되는 가운데 주요국 중앙은행의 통화정책 정상화 등으로 대내외 금리상승 압력이 빠르게 높아지고 있다. 한국은행은 지난해 8월부터 올해 1월까지 총 3차례에 걸쳐 기준금리를 인상한 바 있으며, 경제여건을 감안할 때 연내 추가 인상 가능성이 높은 상황이다.4) 이에 따라 가계대출금리도 상승세가 이어질 전망이다(<그림 Ⅱ-4> 참조). 팬데믹 이후의 가파른 주택가격 상승이 완화적 금융환경에 기인했던 만큼 이러한 금융여건의 긴축적 변화는 가격 변동성 확대 요인으로 작용할 전망이다.
Ⅲ. 금융환경 변화가 주택가격에 미치는 영향 분석
Ⅲ장에서는 금리와 가계대출을 중심으로 금융환경 변화가 주택가격에 미치는 영향을 분석한다. 먼저, 주요 설명변수를 이용하여 주택가격상승률의 변동을 설명하는 모형을 설정한다. 다음으로 충격반응함수를 통해 금리가 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 분석하고, 이를 대출증가율의 영향과 비교해본다. 한편, 팬데믹 이후 주택가격의 불확실성이 크게 높아짐에 따라 꼬리위험5)(tail risk)에 대한 우려가 높다. 이에 분위회귀를 통해 주택가격의 상방 리스크와 하방 리스크를 분석한다.
1. 모형 설정
영국 주택가격상승률을 분석한 Galvao, Montes-Rojas & Park(2013)의 모형을 국내 데이터에 적용하여 금리 및 가계대출이 주택가격에 미치는 영향과 주요 특징을 분석한다. Ⅱ장에서 사용하는 기본 모형은 다음과 같다.
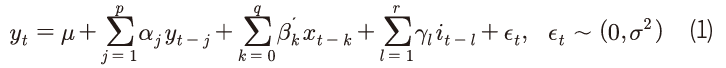
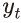 는 KB주택매매가격지수6)를 소비자물가지수로 실질화한 후 로그차분한 실질주택가격상승률을 나타낸다.
는 KB주택매매가격지수6)를 소비자물가지수로 실질화한 후 로그차분한 실질주택가격상승률을 나타낸다. 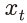 는 주택가격에 영향을 미치는 금리 이외의 설명변수로서 GDP성장률, GDP갭7) 및 실질 가계대출증가율8)을 포함한다. 마지막으로
는 주택가격에 영향을 미치는 금리 이외의 설명변수로서 GDP성장률, GDP갭7) 및 실질 가계대출증가율8)을 포함한다. 마지막으로  는 분기 마지막 월의 평균 1일물 콜금리를 나타낸다.9) 콜금리 데이터가 1991년 이후부터 가용함에 따라 분석기간은 1991년 1분기부터 2021년 3분기이다. BIC(Bayesian Information Criterion)에 따라 p=1, q=0, r=1로 설정하였다.
는 분기 마지막 월의 평균 1일물 콜금리를 나타낸다.9) 콜금리 데이터가 1991년 이후부터 가용함에 따라 분석기간은 1991년 1분기부터 2021년 3분기이다. BIC(Bayesian Information Criterion)에 따라 p=1, q=0, r=1로 설정하였다.
Galvao, Montes-Rojas & Park(2013)은 가계대출이 미치는 영향을 고려하지 않았으나, 국내 부동산시장의 규제조치가 대출규제를 중심으로 시행된 점을 감안하여 실질 가계대출증가율을 설명변수에 추가한다. 실질 가계대출증가율과 콜금리 간 시차(-4~+4분기)상관계수의 최대값은 0.3으로 상관관계가 크게 강하지 않은 것으로 판단된다. 실질 가계대출증가율 대신 GDP대비 가계부채비율을 사용한 경우에도 그 결과는 본 분석의 결과와 큰 차이가 없었다.
2. 충격반응함수 분석
먼저 식(1)에 국소투영법(local projection method)을 적용하여 금리인상에 대한 주택가격의 충격반응함수를 분석한다.10) 본 장에서는 기준금리 75bp 인상 및 실질 가계대출증가율 1%p 축소가 실질 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 살펴본다. 2011년 1분기~2021년 3분기 중 콜금리와 실질 가계대출증가율의 표준편차는 각각 85bp, 1.1%를 기록하였다. 따라서 기준금리 75bp 인상 및 실질 가계대출증가율 1%p 축소는 2011년 이후 콜금리와 실질 가계대출증가율의 약 0.9표준편차 충격이 실질 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 나타낸다.
<그림 Ⅱ-5>는 기준금리 75bp 인상이 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 나타낸다. 금리인상은 주택가격상승률을 낮추는 요인으로 작용하며 그 영향은 시차를 두고 나타난다. 기준금리 75bp 인상은 전국 실질 주택가격상승률을 4년 뒤 평균 1.6%p 낮추는 것으로 추정된다. 금리인상의 영향을 지역별로 살펴보면, 서울(-1.6%p)과 6개 광역시(-1.8%p) 간 차이가 소폭에 그치며 지역 전반에 걸쳐 주택가격상승률이 낮아지는 가운데 서울 내에서도 강북(-1.7%p)과 강남(-1.5%p)의 차이가 크지 않았다. 다만, 아파트의 경우 지역 간 가격상승률 변동폭의 차이가 다소 확대되는 것으로 나타났다.
주택유형별로 나누어 살펴보더라도 금리인상은 주택유형 전반에 걸쳐 가격상승률을 낮추는 것으로 추정된다. 기준금리 75bp 인상 4년 후 연립주택과 단독주택의 가격상승률은 1.7%p씩 낮아지고 아파트의 경우 1.4%p 낮아지는 것으로 추정된다. 서울 지역만을 대상으로 주택유형별 영향을 분석한 경우에도 그 결과는 크게 다르지 않았다.
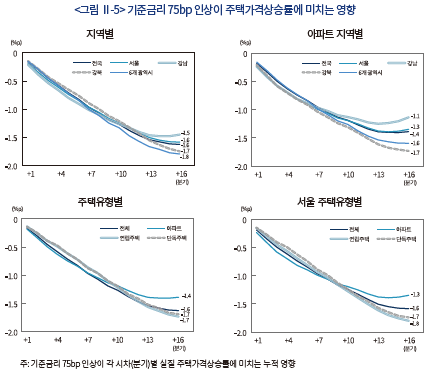
통화정책은 다양한 파급경로를 통해 주택가격에 영향을 미침에 따라 금리인상의 효과는 시차를 두고 점진적으로 나타나는 모습이다. 이로 인해 단기적으로는 가계대출이 금리에 비해 주택가격에 미치는 영향이 큰 것으로 추정된다. <그림 Ⅱ-6>은 기준금리 75bp 인상 및 실질 가계대출증가율 1%p 축소가 실질 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 나타낸다. 기준금리 인상 1년 후 주택가격상승률은 평균 0.6%p 낮아지며, 4년 후에는 그 영향이 -1.6%p로 더욱 확대된다. 반면 실질 가계대출증가율이 1%p 낮아지는 경우, 주택가격상승률에 대한 영향력은 1년 후 –1.0%p로 가장 크게 나타났다가 이후 점차 약화되면서 4년 후에는 그 영향이 대부분 소멸된다. 이러한 결과는 최근 시행되고 있는 가계대출 관리조치가 단기적으로는 주택가격에 미치는 영향이 클 수 있음을 시사한다.
3. 주택가격의 상·하방 리스크 분석
앞에서 살펴본 충격반응함수는 최소자승법(Ordinary Least Squares: OLS)을 통해 분석기간 전체에 걸쳐 평균적으로 기대되는 관계를 추정한다. 그러나 주택시장은 일반적인 재화시장과 달리 수요와 공급의 신축적인 조정이 어려운데, 이로 인해 단기적으로는 주택가격의 불확실성이 높아지며 식(1)이 나타내는 평균적인 관계에서 크게 벗어날 수 있다.
특히, 팬데믹 이후 주택가격이 가파르게 상승하며 주택시장의 불확실성이 크게 높아진 상황이다. 기대보다 큰 폭으로 가격이 상승하는 위험이 높아질 경우, 이에 대응한 경제주체의 행태변화가 오히려 수요를 확대시킴으로써 가격 변동성을 더욱 증폭시킬 수 있다. 이에 따라 불확실성이 높은 상황에서는 평균에 대한 분석보다는 꼬리위험에 대한 분석을 통해 리스크를 효과적으로 이해할 수 있다.
본 장에서는 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 양쪽 꼬리위험에 해당하는 90%분위와 10%분위를 이용하여 주택가격의 상방 리스크와 하방 리스크를 분석하고 최근의 가파른 오름세를 평가한다.11) 조건부 평균을 표현한 식(1)과 동일한 모형에 분위회귀를 적용하여 실질 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 조건부 분위
분위 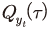 를 식(2)와 같이 추정한다.12)
를 식(2)와 같이 추정한다.12)
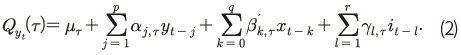
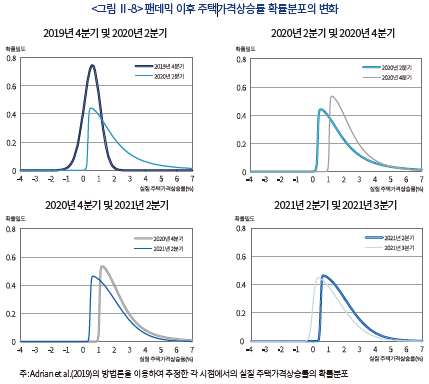
<그림 Ⅱ-7>은 식(2)를 통해 추정한 실질 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 조건부 90%, 10%분위 및 실제 실현값(realized value)의 최근 10년 추이를 나타낸다. 음영의 상단과 하단은 각각 90%분위와 10%분위를 나타내며 음영으로 표시된 영역은 양쪽 꼬리위험 사이의 범위를 나타낸다. 먼저, 팬데믹 이후 주택가격 상승기대가 크게 높아진 것을 확인할 수 있다. 2020년 이전에 비해 90%분위와 10%분위가 모두 높아지며 음영으로 표시된 영역이 가격상승을 의미하는 양(+)의 값에 위치하고 있다. 이와 같은 확률분포의 변화를 쉽게 이해할 수 있도록 <그림 Ⅱ-8>은 각 시점별 횡단면 확률분포를 비교하고 있는데, 팬데믹 이후 전반적인 확률분포가 오른쪽으로 큰 폭 이동하였다. 2021년 이후 주택가격상승률 확률분포가 소폭 왼쪽으로 이동하는 모습이 나타나고 있으나, 팬데믹 이전에 비해 여전히 높은 가격상승 기대가 지속되고 있다.
특히, 하방 리스크에 비해 상방 리스크가 빠르게 높아짐에 따라 주택가격의 하락 가능성은 낮아진 반면 단기 급등 가능성이 높아졌다. 상방 리스크를 의미하는 90%분위는 2012~2019년 평균 +1.2%에서 2020년 이후에는 +3.2%로 큰 폭(+2.0%p) 상승하였다. 이에 반해 10%분위는 같은 기간 상승폭이 1.1%p(-0.5% → +0.6%)에 그치며 상방 리스크가 비대칭적으로 높아진 상황이다. <그림 Ⅱ-8>에서 확인할 수 있듯이 팬데믹 이후 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 오른쪽 꼬리(right tail)가 길어진 모습인데 확률분포의 왜도(skewness) 추정값이 2019년 평균 –0.3에서 2020년 이후에는 1.5로 크게 증가하였다.
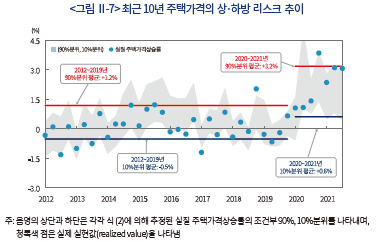
최근의 주택가격상승률은 확률분포의 오른쪽 꼬리(90%분위)에 가까운 실현값이 이어지고 있는데 이는 주택시장의 과열 양상을 반영하는 것으로 판단된다. <그림 Ⅱ-7>에서 음영으로 표시된 영역은 10%, 90%분위의 범위를 나타내는데, 보통의 경우 주택가격상승률은 해당 영역의 중앙을 중심으로 실현값이 나타난다. 그러나 2020년 4분기부터 90%분위에 가까운 실현값이 이어지며 기대수준에 비해 크게 높은 주택가격 상승세가 지속되고 있다.
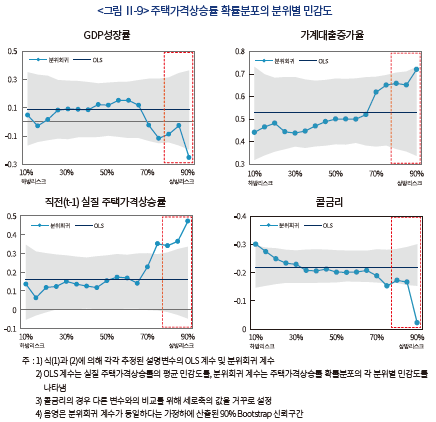
확률분포의 분위별 민감도를 살펴봄으로써 주택가격의 상방 리스크가 어떤 요인에 의해 확대되었는가를 확인할 수 있다. <그림 Ⅱ-9>는 식(1)을 통해 추정한 각 설명변수의 OLS 계수와 식(2)를 통해 추정한 분위별 계수를 나타낸다. OLS 계수는 주택가격상승률의 평균 민감도를, 분위회귀 계수는 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 각 분위별 민감도를 의미한다. 설명변수가 상·하방 리스크 확대요인으로 작용하지 않는 경우, OLS 계수와 분위별 계수가 동일한 값을 가지며 확률분포 전반에 동일한 영향을 미친다. 반면 설명변수가 상방 리스크 확대요인으로 작용하는 경우에는 90%분위 계수가 OLS 계수보다 더 큰 절대값을 나타내며 확률분포의 오른쪽 꼬리에 더 크게 영향을 미친다. 따라서 OLS 계수와 90%분위 계수 간 비교를 통해 상방 리스크의 확대요인을 살펴볼 수 있다.
먼저 가계대출증가율의 90%분위 계수(0.72)가 OLS 계수(0.53)보다 더 큰 값을 나타내는데, 주택가격의 상방 리스크가 가계대출에 더 민감하게 반응함을 확인할 수 있다. 팬데믹 이후 가파른 가계대출 증가세가 이어졌음을 고려할 때 유동성 요인이 상방 리스크 확대를 유발한 것으로 판단된다. 이에 따라 가계대출 증가가 주택가격 상승을 유발하고, 주택가격 상승이 다시 대출수요 확대로 이어지는 가계부채와 주택가격 간 피드백(feedback) 효과가 2020년 이후 더욱 강하게 작용하고 있는 것으로 판단된다.13)
직전(t-1) 주택가격상승률도 90%분위 계수(0.47)가 OLS 계수(0.16)에 비해 높은 민감도를 나타낸다. 이와 같은 결과는 주택시장이 과열양상을 보일수록 가격 오름세가 미래 가격상승 기대를 더 강화시키는 것으로 해석할 수 있다. 따라서 가격의 모멘텀(momentum) 요인 역시 팬데믹 이후 주택가격의 상방 리스크를 확대시킴으로써 주택가격 급등을 유발한 것으로 판단된다.
반면 상방 리스크는 금리에 대한 민감도가 상대적으로 낮은 것으로 나타난다. 금리상승은 주택가격상승률을 낮추는 요인으로 작용함에 따라 콜금리의 OLS 계수와 분위별 계수가 모두 음(-)의 값으로 추정되는 가운데 90%분위 계수(-0.02)가 OLS 계수(-0.22)에 비해 낮은 민감도를 나타낸다.14) 이러한 결과는 상방 리스크가 크게 높아진 상황에서는 금리인상이 가격 급등세 억제에 미치는 영향력이 크지 않을 수 있음을 시사한다. 한편, 콜금리의 분위계수 중 하방 리스크를 의미하는 10%분위 계수(-0.30)가 가장 높은 민감도를 나타내고 있다. 이는 금리인상이 주택가격의 하방 리스크 확대요인으로 더 크게 작용할 수 있음을 의미한다.
Ⅳ. 요약 및 시사점
완화적 금융환경을 바탕으로 팬데믹 이후 주택가격이 상당히 가파른 속도로 상승하였다. 이러한 가격 상승세는 가계대출 증가에 따른 유동성 요인과 가격 오름세에 따른 모멘텀 요인이 주택가격의 상방 리스크를 확대시킨 데 기인하는 것으로 판단된다.
인플레이션 압력이 증대됨에 따라 금리인상 등 금융환경의 긴축적 변화가 이어질 것으로 예상된다. 기준금리 인상은 주택시장 전반의 가격상승률을 낮추는 요인으로 작용하며 그 영향은 시차를 두고 점진적으로 나타난다.15) 다만, 현재 주택시장은 가격의 상방 리스크가 크게 확대되는 등 불확실성이 높은 상황이므로 단기적으로는 주택가격 조정압력이 제한적일 수 있다.
분석 결과를 종합하여 주택시장에 대한 장·단기 대응과제를 살펴보면 다음과 같다. 단기적으로는 가계대출 관리를 중심으로 주택가격의 상방 리스크에 대응할 필요가 있다. 앞에서 살펴보았듯이 상방 리스크가 크게 높아진 현재 상황에서는 가계대출 관리조치가 금리인상에 비해 가격 급등세 억제에 더 효과적으로 작용하는 것으로 판단되기 때문이다. 다만, 이 과정에서 취약계층 등 실수요자가 자금조달에 어려움을 겪지 않도록 관리가 필요하다.
장기적 대응과제로는 금리인상의 파급효과를 감안하여 대출관리 강화조치의 점진적인 정상화를 고려할 필요가 있다. 한국은행의 금리인상 기조는 장기적으로 주택가격의 하방 압력으로 작용할 전망이다. 특히, 작년 8월부터 진행되고 있는 기준금리 인상 사이클은 2011년 하반기 이후 가장 빠른 속도로 진행되고 있어 주택가격의 하방 리스크가 높아질 가능성이 크다. 가계부채비율이 그 어느 때보다 높은 상황에서 주택시장의 충격은 실물경기 위축으로 이어질 위험이 크다. 따라서 주택가격의 상방 리스크가 완화되는 경우 대출 총량관리 조치의 정상화를 검토할 필요가 있다. 이를 위해 주택가격과 대출 증가세에 대한 지속적인 모니터링이 요구된다. 한편 가계도 주택가격의 하방 리스크에 유의할 필요가 있으며, 가격상승 기대를 바탕으로 과도한 대출을 수반하는 주택거래를 지양해야 한다.
<부록> 분위(quantile)의 개념
분위(또는 분위수)는 확률분포를 일정비율로 나누는 경계값을 의미한다. <부록 그림 1>은 표준정규분포의 90%분위를 설명하고 있는데, 해당 값보다 작은 값이 실현될 확률이 90%인 경계값에 해당한다. 90%분위보다 큰 값이 실현될 확률이 10%에 불과하기 때문에 90%분위는 확률분포의 상방 리스크(upside risk), 즉 오른쪽 꼬리위험을 나타낸다. <부록 그림 2>는 표준정규분포의 10%분위를 나타내고 있는데 90%분위와 마찬가지로 해당 값보다 작은 값이 실현될 확률이 10%인 경계값을 의미함에 따라 하방 리스크, 즉 왼쪽 꼬리위험을 나타낸다.
리스크 관리에서 널리 사용되고 있는 VaR(Value at Risk)도 분위의 개념에 해당하는데 1% VaR는 금융자산수익률 확률분포의 1%분위를 의미한다. 다만, VaR는 발생 가능한 손실을 분석하기 위한 도구로 사용됨에 따라 주로 금융자산수익률 확률분포의 하방 리스크를 분석한다.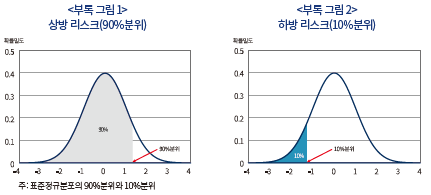
1) 노르웨이, 뉴질랜드, 영국 등 주요국 중앙은행이 지난해부터 정책금리를 인상해오고 있으며, 미 연준도 올해 정책금리를 빠른 속도로 인상할 전망이다.
2) The Economist(2022. 3. 2)는 국제적 기준 및 과거 추세와 비교해볼 때, 현재 우리나라 부동산 가치가 경제규모 대비 높은 수준임을 지적하며 대차대조표 불황(balance-sheet recession) 가능성을 언급하였다.
3) 예상보다 빠른 경기회복, 재정지원 확대, 저축률 상승 등 경제적 요인과 팬데믹으로 인한 주거 공간 수요 증가, 공급제약 등 수급적 요인에 기인하여 주택수요가 늘어난 가운데, 매우 용이한 자금조달 여건이 주택수요를 더욱 증가시켰다(Igan, Kohlscheen & Rungcharoenkitkul, 2022).
4) “코로나19 관련 불확실성이 상존하고 있으나 국내경제가 양호한 성장세를 지속하고 물가가 상당기간 목표수준을 상회할 것으로 예상되므로, 앞으로 통화정책의 완화 정도를 적절히 조정해 나갈 것이다.”(한국은행, 2022. 2. 24, 통화정책방향)
5) 발생 가능성은 낮으나 실현될 경우 주택가격이 기대보다 큰 폭으로 상승 또는 하락할 위험을 의미한다.
6) 한국부동산원도 주택매매가격지수를 발표하고 있으나 2003년 11월 이후부터 데이터가 존재함에 따라 KB주택매매가격지수에 비해 가용 샘플이 상대적으로 적다.
7) GDP갭은 Grant & Chan(2017)의 방법론을 사용하여 추정하였다.
8) 자금순환표 ‘가계 및 비영리단체’의 부채를 소비자물가지수로 실질화하여 산출하였다. SNA(System of National Accounts) 기준연도별 시계열 단절이 존재함에 따라 이용가능한 데이터의 가장 최근 기준년 자료를 사용하였다.
9) 본 보고서는 거시금융 변수를 중심으로 주택가격 분석모형을 설정하였다. 그러나 모형에서 고려한 변수 이외에도 다양한 요인(인구통계학적 요인, 주택수급 요인 등)이 주택가격에 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로 이에 따른 분석의 한계가 존재한다.
10) 식(1)의 종속변수를 (t)기~(t+h)기 중 실질 주택가격상승률을 나타내는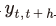 로 사용하여 다음의 모형을 추정한다.
로 사용하여 다음의 모형을 추정한다.
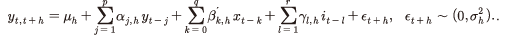 11) 분위회귀를 통한 연구들은 주로 금융·경제 변수의 95%, 5%분위를 사용하여 상·하방 리스크를 분석하고 있다. 그러나 본 분석에서 사용할 수 있는 관측값의 수(n=123)가 적음에 따라 95%, 5%분위에 대한 추정의 안정성이 낮을 위험이 있다. 이에 따라 추정 안정성이 상대적으로 높은 90%, 10%분위를 사용한다. 분위의 개념은 <부록>을 참고하기 바란다.
11) 분위회귀를 통한 연구들은 주로 금융·경제 변수의 95%, 5%분위를 사용하여 상·하방 리스크를 분석하고 있다. 그러나 본 분석에서 사용할 수 있는 관측값의 수(n=123)가 적음에 따라 95%, 5%분위에 대한 추정의 안정성이 낮을 위험이 있다. 이에 따라 추정 안정성이 상대적으로 높은 90%, 10%분위를 사용한다. 분위의 개념은 <부록>을 참고하기 바란다.
12) 추정에 대한 구체적인 방법론은 Koenker & Bassett(1978) 및 Galvao, Montes-Rojas & Park(2013)을 참조하기 바란다.
13) Alter, Feng & Valckx(2018)는 27개국을 대상으로 패널 VAR 분석을 통해 가계부채의 증가가 주택가격 상승을 유발하고, 이는 다시 가계부채의 증가로 이어지는 것을 확인하였다. 이러한 동태적 관계는 가계부채와 주택가격 간 피드백(feedback) 효과가 존재함을 의미한다.
14) 콜금리의 경우 주택가격상승률에 음(-)의 영향을 미치므로 추정계수가 작을수록 높은 민감도를 의미한다. 이에 따라 <그림 Ⅱ-9>의 오른쪽 하단 그림에서 높은 민감도가 상단에 위치하도록 세로축의 값을 거꾸로 설정하였다.
15) Igan, Kohlscheen & Rungcharoenkitkul(2022)은 팬데믹 이후의 주택시장 전개 양상이 이례적이었음을 지적하고 완만한 금리인상이 투기수요 억제에 도움이 될 수 있음을 강조하였다.
참고문헌
한국은행, 2022. 2. 24, 『통화정책방향』.
Adrian, T., Boyarchenko, N., Giannone, D., 2019, Vulnerable growth, American Economic Review 109(4), 1263-1289.
Alter, A., Feng, A.X., Valckx, N., 2018, Understanding the macro-financial effects of household debt: A global perspective, IMF working paper WP/18/76.
Galvao Jr, A.F., Montes-Rojas, G., Park, S.Y., 2013, Quantile autoregressive distributed lag model with an application to house price returns, Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics 75(2), 307-321.
Grant, A.L., Chan, J.C., 2017, Reconciling output gaps: Unobserved components model and Hodrick-Prescott filter, Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 75, 114-121.
Igan, D., Kohlscheen, E., Rungcharoenkitkul, P., 2022, Housing Market Risks in the Wake of the Pandemic, BIS Bulletin No.50.
Koenker, R., Bassett, G., 1978, Regression quantiles, Econometrica 46(1), 33-50.
The Economist, 2022. 3. 2, South Korea’s economy threatens to become like Japan’s.
코로나19의 경제적 충격에 대응하여 각국 중앙은행은 통화정책을 상당히 완화적으로 운용하였으며 이를 통해 금융시장 안정 및 실물경제 회복에 크게 기여하였다. 그러나 2021년 하반기 이후 인플레이션 우려가 높아짐에 따라 주요국 중앙은행은 정책금리 인상1), 자산매입 종료 등을 통해 통화정책을 빠르게 정상화하는 추세이다.
국내 금융시장도 작년 8월부터 한국은행의 금리인상 기조가 이어지면서 완화적 금융여건이 축소되고 있다. 이러한 금융환경 변화가 자산시장, 특히 주택시장에 미칠 영향에 관심이 높아지고 있다.2) 대부분의 주택매매에서 레버리지가 활용됨에 따라 금융여건의 변화는 주택시장 변동의 주요인으로 작용한다. 팬데믹 이후 주택관련 대출을 중심으로 가계부채가 빠르게 늘어난 가운데 주택가격이 가파른 상승세를 기록하는 등 주택시장을 중심으로 금융불균형에 대한 우려가 높은 상황이다. 따라서 최근 주택시장 변화에 대한 이해는 거시금융안정성 측면에서 중요한 의미를 가진다.
본고에서는 금융환경의 긴축적 변화가 주택시장에 미치는 영향을 분석하고 시사점을 제시하고자 한다. 본 보고서의 구성은 다음과 같다. Ⅱ장에서는 팬데믹 이후 주택가격 추이와 최근 금융환경의 변화를 살펴본다. Ⅲ장에서는 금융환경 변화가 주택가격에 미치는 영향을 분석한다. 먼저 금리인상이 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 분석하고 가계대출의 영향과 비교해본다. 한편 주택시장의 경우, 수요와 공급의 신축적인 조정이 어려워 단기적으로는 가격 변동성이 크게 높아질 수 있다. 팬데믹 이후 주택시장의 불확실성이 크게 높아진 점을 감안하여 분위회귀(quantile regression)를 통해 주택가격의 상방 리스크(upside risk)와 하방 리스크(downside risk)를 분석한다. 마지막 Ⅳ장에서는 분석 내용을 바탕으로 정책적 시사점을 도출한다.
Ⅱ. 팬데믹 이후 주택시장 추이
<그림 Ⅱ-1>에 나타난 바와 같이 팬데믹 이후 가계신용이 소비활동에 비해 빠른 속도로 증가하였다. 부채를 통해 늘어난 가계의 유동성은 실물경제로 순환되기보다는 대체로 자산시장으로 유입된 것으로 판단된다. 특히, 부동산시장으로의 자금 유입이 크게 늘어나면서 2020년 이후 주택가격은 과거 추세에 비해 상당히 가파르게 상승하였다(<그림 Ⅱ-2> 참조). 2020~2021년 중 전국 주택매매가격지수와 아파트매매가격지수는 각각 24.6%, 31.8% 상승하였는데, 이는 직전 10년 상승률(2009~2019년 중 각각 23.6%, 27.9%)을 상회한다.

목표수준을 상회하는 물가상승세가 지속되는 가운데 주요국 중앙은행의 통화정책 정상화 등으로 대내외 금리상승 압력이 빠르게 높아지고 있다. 한국은행은 지난해 8월부터 올해 1월까지 총 3차례에 걸쳐 기준금리를 인상한 바 있으며, 경제여건을 감안할 때 연내 추가 인상 가능성이 높은 상황이다.4) 이에 따라 가계대출금리도 상승세가 이어질 전망이다(<그림 Ⅱ-4> 참조). 팬데믹 이후의 가파른 주택가격 상승이 완화적 금융환경에 기인했던 만큼 이러한 금융여건의 긴축적 변화는 가격 변동성 확대 요인으로 작용할 전망이다.

Ⅲ장에서는 금리와 가계대출을 중심으로 금융환경 변화가 주택가격에 미치는 영향을 분석한다. 먼저, 주요 설명변수를 이용하여 주택가격상승률의 변동을 설명하는 모형을 설정한다. 다음으로 충격반응함수를 통해 금리가 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 분석하고, 이를 대출증가율의 영향과 비교해본다. 한편, 팬데믹 이후 주택가격의 불확실성이 크게 높아짐에 따라 꼬리위험5)(tail risk)에 대한 우려가 높다. 이에 분위회귀를 통해 주택가격의 상방 리스크와 하방 리스크를 분석한다.
1. 모형 설정
영국 주택가격상승률을 분석한 Galvao, Montes-Rojas & Park(2013)의 모형을 국내 데이터에 적용하여 금리 및 가계대출이 주택가격에 미치는 영향과 주요 특징을 분석한다. Ⅱ장에서 사용하는 기본 모형은 다음과 같다.
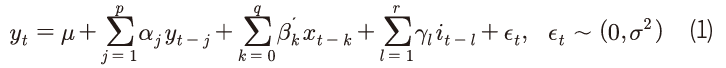
Galvao, Montes-Rojas & Park(2013)은 가계대출이 미치는 영향을 고려하지 않았으나, 국내 부동산시장의 규제조치가 대출규제를 중심으로 시행된 점을 감안하여 실질 가계대출증가율을 설명변수에 추가한다. 실질 가계대출증가율과 콜금리 간 시차(-4~+4분기)상관계수의 최대값은 0.3으로 상관관계가 크게 강하지 않은 것으로 판단된다. 실질 가계대출증가율 대신 GDP대비 가계부채비율을 사용한 경우에도 그 결과는 본 분석의 결과와 큰 차이가 없었다.
2. 충격반응함수 분석
먼저 식(1)에 국소투영법(local projection method)을 적용하여 금리인상에 대한 주택가격의 충격반응함수를 분석한다.10) 본 장에서는 기준금리 75bp 인상 및 실질 가계대출증가율 1%p 축소가 실질 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 살펴본다. 2011년 1분기~2021년 3분기 중 콜금리와 실질 가계대출증가율의 표준편차는 각각 85bp, 1.1%를 기록하였다. 따라서 기준금리 75bp 인상 및 실질 가계대출증가율 1%p 축소는 2011년 이후 콜금리와 실질 가계대출증가율의 약 0.9표준편차 충격이 실질 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 나타낸다.
<그림 Ⅱ-5>는 기준금리 75bp 인상이 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 나타낸다. 금리인상은 주택가격상승률을 낮추는 요인으로 작용하며 그 영향은 시차를 두고 나타난다. 기준금리 75bp 인상은 전국 실질 주택가격상승률을 4년 뒤 평균 1.6%p 낮추는 것으로 추정된다. 금리인상의 영향을 지역별로 살펴보면, 서울(-1.6%p)과 6개 광역시(-1.8%p) 간 차이가 소폭에 그치며 지역 전반에 걸쳐 주택가격상승률이 낮아지는 가운데 서울 내에서도 강북(-1.7%p)과 강남(-1.5%p)의 차이가 크지 않았다. 다만, 아파트의 경우 지역 간 가격상승률 변동폭의 차이가 다소 확대되는 것으로 나타났다.

통화정책은 다양한 파급경로를 통해 주택가격에 영향을 미침에 따라 금리인상의 효과는 시차를 두고 점진적으로 나타나는 모습이다. 이로 인해 단기적으로는 가계대출이 금리에 비해 주택가격에 미치는 영향이 큰 것으로 추정된다. <그림 Ⅱ-6>은 기준금리 75bp 인상 및 실질 가계대출증가율 1%p 축소가 실질 주택가격상승률에 미치는 영향을 나타낸다. 기준금리 인상 1년 후 주택가격상승률은 평균 0.6%p 낮아지며, 4년 후에는 그 영향이 -1.6%p로 더욱 확대된다. 반면 실질 가계대출증가율이 1%p 낮아지는 경우, 주택가격상승률에 대한 영향력은 1년 후 –1.0%p로 가장 크게 나타났다가 이후 점차 약화되면서 4년 후에는 그 영향이 대부분 소멸된다. 이러한 결과는 최근 시행되고 있는 가계대출 관리조치가 단기적으로는 주택가격에 미치는 영향이 클 수 있음을 시사한다.

앞에서 살펴본 충격반응함수는 최소자승법(Ordinary Least Squares: OLS)을 통해 분석기간 전체에 걸쳐 평균적으로 기대되는 관계를 추정한다. 그러나 주택시장은 일반적인 재화시장과 달리 수요와 공급의 신축적인 조정이 어려운데, 이로 인해 단기적으로는 주택가격의 불확실성이 높아지며 식(1)이 나타내는 평균적인 관계에서 크게 벗어날 수 있다.
특히, 팬데믹 이후 주택가격이 가파르게 상승하며 주택시장의 불확실성이 크게 높아진 상황이다. 기대보다 큰 폭으로 가격이 상승하는 위험이 높아질 경우, 이에 대응한 경제주체의 행태변화가 오히려 수요를 확대시킴으로써 가격 변동성을 더욱 증폭시킬 수 있다. 이에 따라 불확실성이 높은 상황에서는 평균에 대한 분석보다는 꼬리위험에 대한 분석을 통해 리스크를 효과적으로 이해할 수 있다.
본 장에서는 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 양쪽 꼬리위험에 해당하는 90%분위와 10%분위를 이용하여 주택가격의 상방 리스크와 하방 리스크를 분석하고 최근의 가파른 오름세를 평가한다.11) 조건부 평균을 표현한 식(1)과 동일한 모형에 분위회귀를 적용하여 실질 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 조건부
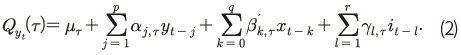
특히, 하방 리스크에 비해 상방 리스크가 빠르게 높아짐에 따라 주택가격의 하락 가능성은 낮아진 반면 단기 급등 가능성이 높아졌다. 상방 리스크를 의미하는 90%분위는 2012~2019년 평균 +1.2%에서 2020년 이후에는 +3.2%로 큰 폭(+2.0%p) 상승하였다. 이에 반해 10%분위는 같은 기간 상승폭이 1.1%p(-0.5% → +0.6%)에 그치며 상방 리스크가 비대칭적으로 높아진 상황이다. <그림 Ⅱ-8>에서 확인할 수 있듯이 팬데믹 이후 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 오른쪽 꼬리(right tail)가 길어진 모습인데 확률분포의 왜도(skewness) 추정값이 2019년 평균 –0.3에서 2020년 이후에는 1.5로 크게 증가하였다.


확률분포의 분위별 민감도를 살펴봄으로써 주택가격의 상방 리스크가 어떤 요인에 의해 확대되었는가를 확인할 수 있다. <그림 Ⅱ-9>는 식(1)을 통해 추정한 각 설명변수의 OLS 계수와 식(2)를 통해 추정한 분위별 계수를 나타낸다. OLS 계수는 주택가격상승률의 평균 민감도를, 분위회귀 계수는 주택가격상승률 확률분포의 각 분위별 민감도를 의미한다. 설명변수가 상·하방 리스크 확대요인으로 작용하지 않는 경우, OLS 계수와 분위별 계수가 동일한 값을 가지며 확률분포 전반에 동일한 영향을 미친다. 반면 설명변수가 상방 리스크 확대요인으로 작용하는 경우에는 90%분위 계수가 OLS 계수보다 더 큰 절대값을 나타내며 확률분포의 오른쪽 꼬리에 더 크게 영향을 미친다. 따라서 OLS 계수와 90%분위 계수 간 비교를 통해 상방 리스크의 확대요인을 살펴볼 수 있다.
먼저 가계대출증가율의 90%분위 계수(0.72)가 OLS 계수(0.53)보다 더 큰 값을 나타내는데, 주택가격의 상방 리스크가 가계대출에 더 민감하게 반응함을 확인할 수 있다. 팬데믹 이후 가파른 가계대출 증가세가 이어졌음을 고려할 때 유동성 요인이 상방 리스크 확대를 유발한 것으로 판단된다. 이에 따라 가계대출 증가가 주택가격 상승을 유발하고, 주택가격 상승이 다시 대출수요 확대로 이어지는 가계부채와 주택가격 간 피드백(feedback) 효과가 2020년 이후 더욱 강하게 작용하고 있는 것으로 판단된다.13)
직전(t-1) 주택가격상승률도 90%분위 계수(0.47)가 OLS 계수(0.16)에 비해 높은 민감도를 나타낸다. 이와 같은 결과는 주택시장이 과열양상을 보일수록 가격 오름세가 미래 가격상승 기대를 더 강화시키는 것으로 해석할 수 있다. 따라서 가격의 모멘텀(momentum) 요인 역시 팬데믹 이후 주택가격의 상방 리스크를 확대시킴으로써 주택가격 급등을 유발한 것으로 판단된다.
반면 상방 리스크는 금리에 대한 민감도가 상대적으로 낮은 것으로 나타난다. 금리상승은 주택가격상승률을 낮추는 요인으로 작용함에 따라 콜금리의 OLS 계수와 분위별 계수가 모두 음(-)의 값으로 추정되는 가운데 90%분위 계수(-0.02)가 OLS 계수(-0.22)에 비해 낮은 민감도를 나타낸다.14) 이러한 결과는 상방 리스크가 크게 높아진 상황에서는 금리인상이 가격 급등세 억제에 미치는 영향력이 크지 않을 수 있음을 시사한다. 한편, 콜금리의 분위계수 중 하방 리스크를 의미하는 10%분위 계수(-0.30)가 가장 높은 민감도를 나타내고 있다. 이는 금리인상이 주택가격의 하방 리스크 확대요인으로 더 크게 작용할 수 있음을 의미한다.

완화적 금융환경을 바탕으로 팬데믹 이후 주택가격이 상당히 가파른 속도로 상승하였다. 이러한 가격 상승세는 가계대출 증가에 따른 유동성 요인과 가격 오름세에 따른 모멘텀 요인이 주택가격의 상방 리스크를 확대시킨 데 기인하는 것으로 판단된다.
인플레이션 압력이 증대됨에 따라 금리인상 등 금융환경의 긴축적 변화가 이어질 것으로 예상된다. 기준금리 인상은 주택시장 전반의 가격상승률을 낮추는 요인으로 작용하며 그 영향은 시차를 두고 점진적으로 나타난다.15) 다만, 현재 주택시장은 가격의 상방 리스크가 크게 확대되는 등 불확실성이 높은 상황이므로 단기적으로는 주택가격 조정압력이 제한적일 수 있다.
분석 결과를 종합하여 주택시장에 대한 장·단기 대응과제를 살펴보면 다음과 같다. 단기적으로는 가계대출 관리를 중심으로 주택가격의 상방 리스크에 대응할 필요가 있다. 앞에서 살펴보았듯이 상방 리스크가 크게 높아진 현재 상황에서는 가계대출 관리조치가 금리인상에 비해 가격 급등세 억제에 더 효과적으로 작용하는 것으로 판단되기 때문이다. 다만, 이 과정에서 취약계층 등 실수요자가 자금조달에 어려움을 겪지 않도록 관리가 필요하다.
장기적 대응과제로는 금리인상의 파급효과를 감안하여 대출관리 강화조치의 점진적인 정상화를 고려할 필요가 있다. 한국은행의 금리인상 기조는 장기적으로 주택가격의 하방 압력으로 작용할 전망이다. 특히, 작년 8월부터 진행되고 있는 기준금리 인상 사이클은 2011년 하반기 이후 가장 빠른 속도로 진행되고 있어 주택가격의 하방 리스크가 높아질 가능성이 크다. 가계부채비율이 그 어느 때보다 높은 상황에서 주택시장의 충격은 실물경기 위축으로 이어질 위험이 크다. 따라서 주택가격의 상방 리스크가 완화되는 경우 대출 총량관리 조치의 정상화를 검토할 필요가 있다. 이를 위해 주택가격과 대출 증가세에 대한 지속적인 모니터링이 요구된다. 한편 가계도 주택가격의 하방 리스크에 유의할 필요가 있으며, 가격상승 기대를 바탕으로 과도한 대출을 수반하는 주택거래를 지양해야 한다.
<부록> 분위(quantile)의 개념
분위(또는 분위수)는 확률분포를 일정비율로 나누는 경계값을 의미한다. <부록 그림 1>은 표준정규분포의 90%분위를 설명하고 있는데, 해당 값보다 작은 값이 실현될 확률이 90%인 경계값에 해당한다. 90%분위보다 큰 값이 실현될 확률이 10%에 불과하기 때문에 90%분위는 확률분포의 상방 리스크(upside risk), 즉 오른쪽 꼬리위험을 나타낸다. <부록 그림 2>는 표준정규분포의 10%분위를 나타내고 있는데 90%분위와 마찬가지로 해당 값보다 작은 값이 실현될 확률이 10%인 경계값을 의미함에 따라 하방 리스크, 즉 왼쪽 꼬리위험을 나타낸다.
리스크 관리에서 널리 사용되고 있는 VaR(Value at Risk)도 분위의 개념에 해당하는데 1% VaR는 금융자산수익률 확률분포의 1%분위를 의미한다. 다만, VaR는 발생 가능한 손실을 분석하기 위한 도구로 사용됨에 따라 주로 금융자산수익률 확률분포의 하방 리스크를 분석한다.

1) 노르웨이, 뉴질랜드, 영국 등 주요국 중앙은행이 지난해부터 정책금리를 인상해오고 있으며, 미 연준도 올해 정책금리를 빠른 속도로 인상할 전망이다.
2) The Economist(2022. 3. 2)는 국제적 기준 및 과거 추세와 비교해볼 때, 현재 우리나라 부동산 가치가 경제규모 대비 높은 수준임을 지적하며 대차대조표 불황(balance-sheet recession) 가능성을 언급하였다.
3) 예상보다 빠른 경기회복, 재정지원 확대, 저축률 상승 등 경제적 요인과 팬데믹으로 인한 주거 공간 수요 증가, 공급제약 등 수급적 요인에 기인하여 주택수요가 늘어난 가운데, 매우 용이한 자금조달 여건이 주택수요를 더욱 증가시켰다(Igan, Kohlscheen & Rungcharoenkitkul, 2022).
4) “코로나19 관련 불확실성이 상존하고 있으나 국내경제가 양호한 성장세를 지속하고 물가가 상당기간 목표수준을 상회할 것으로 예상되므로, 앞으로 통화정책의 완화 정도를 적절히 조정해 나갈 것이다.”(한국은행, 2022. 2. 24, 통화정책방향)
5) 발생 가능성은 낮으나 실현될 경우 주택가격이 기대보다 큰 폭으로 상승 또는 하락할 위험을 의미한다.
6) 한국부동산원도 주택매매가격지수를 발표하고 있으나 2003년 11월 이후부터 데이터가 존재함에 따라 KB주택매매가격지수에 비해 가용 샘플이 상대적으로 적다.
7) GDP갭은 Grant & Chan(2017)의 방법론을 사용하여 추정하였다.
8) 자금순환표 ‘가계 및 비영리단체’의 부채를 소비자물가지수로 실질화하여 산출하였다. SNA(System of National Accounts) 기준연도별 시계열 단절이 존재함에 따라 이용가능한 데이터의 가장 최근 기준년 자료를 사용하였다.
9) 본 보고서는 거시금융 변수를 중심으로 주택가격 분석모형을 설정하였다. 그러나 모형에서 고려한 변수 이외에도 다양한 요인(인구통계학적 요인, 주택수급 요인 등)이 주택가격에 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로 이에 따른 분석의 한계가 존재한다.
10) 식(1)의 종속변수를 (t)기~(t+h)기 중 실질 주택가격상승률을 나타내는
12) 추정에 대한 구체적인 방법론은 Koenker & Bassett(1978) 및 Galvao, Montes-Rojas & Park(2013)을 참조하기 바란다.
13) Alter, Feng & Valckx(2018)는 27개국을 대상으로 패널 VAR 분석을 통해 가계부채의 증가가 주택가격 상승을 유발하고, 이는 다시 가계부채의 증가로 이어지는 것을 확인하였다. 이러한 동태적 관계는 가계부채와 주택가격 간 피드백(feedback) 효과가 존재함을 의미한다.
14) 콜금리의 경우 주택가격상승률에 음(-)의 영향을 미치므로 추정계수가 작을수록 높은 민감도를 의미한다. 이에 따라 <그림 Ⅱ-9>의 오른쪽 하단 그림에서 높은 민감도가 상단에 위치하도록 세로축의 값을 거꾸로 설정하였다.
15) Igan, Kohlscheen & Rungcharoenkitkul(2022)은 팬데믹 이후의 주택시장 전개 양상이 이례적이었음을 지적하고 완만한 금리인상이 투기수요 억제에 도움이 될 수 있음을 강조하였다.
참고문헌
한국은행, 2022. 2. 24, 『통화정책방향』.
Adrian, T., Boyarchenko, N., Giannone, D., 2019, Vulnerable growth, American Economic Review 109(4), 1263-1289.
Alter, A., Feng, A.X., Valckx, N., 2018, Understanding the macro-financial effects of household debt: A global perspective, IMF working paper WP/18/76.
Galvao Jr, A.F., Montes-Rojas, G., Park, S.Y., 2013, Quantile autoregressive distributed lag model with an application to house price returns, Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics 75(2), 307-321.
Grant, A.L., Chan, J.C., 2017, Reconciling output gaps: Unobserved components model and Hodrick-Prescott filter, Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 75, 114-121.
Igan, D., Kohlscheen, E., Rungcharoenkitkul, P., 2022, Housing Market Risks in the Wake of the Pandemic, BIS Bulletin No.50.
Koenker, R., Bassett, G., 1978, Regression quantiles, Econometrica 46(1), 33-50.
The Economist, 2022. 3. 2, South Korea’s economy threatens to become like Japan’s.
